Cuprins
The starry sky has always fascinated mankind. Stargazing, or stargazing, is an activity that connects you with the universe and gives you a unique perspective on our place in the cosmos. From ancient astronomers to modern-day enthusiasts, gazing at the starry sky has sparked curiosity and inspired discoveries.
One of the most impressive objects visible in the night sky is the Milky Way. This bright streak across the celestial vault is actually our galaxy seen from within. On clear, dark nights, the Milky Way appears as a diffuse streak of light, dotted with millions of stars.
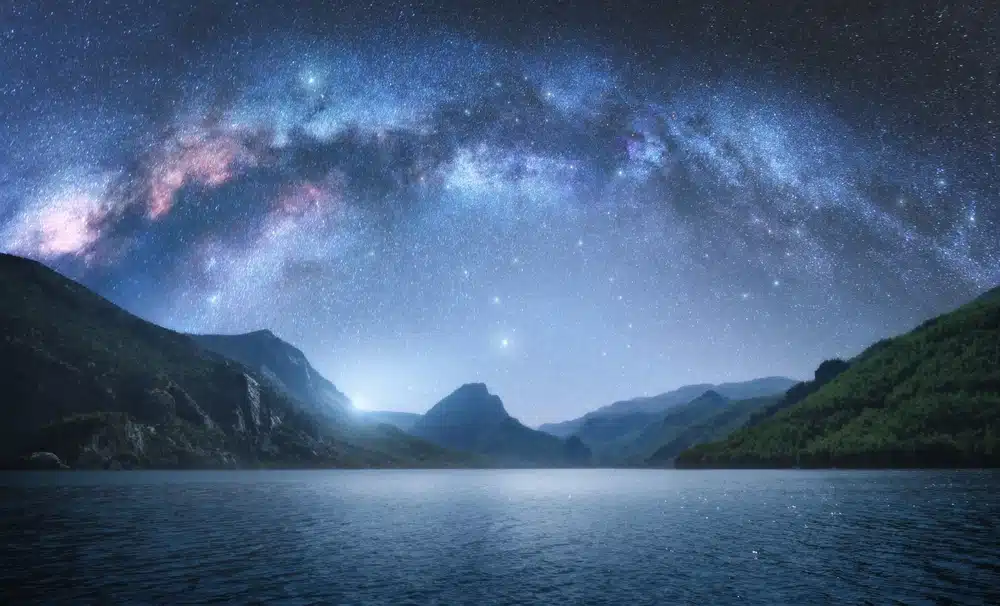

The Milky Way shining over the mountains
The Moon is another fascinating cosmic object. As the closest celestial body to Earth, the Moon can be studied in detail even without special instruments.
The craters and formations on the Moon’s surface are a spectacular sight.
To explore the wonders of the night sky in depth, a telescope is the ideal instrument. It allows you to observe distant planets, nebulae and galaxies.
Even a small telescope can reveal amazing details of celestial objects.
Stargazing is an activity accessible to anyone, regardless of age or experience. All you need is curiosity, patience and a clear sky.
As you learn to recognize constellations and celestial objects, you’ll discover the beauty and mysteries of the universe. Discover our guide to stargazing below.
- Equipment needed for stargazing
- Observing the Moon – our fascinating cosmic neighbor
- Exploring the Milky Way – our home galaxy
- Spectacular astronomical phenomena – eclipses and meteor showers
- The best locations for stargazing in Romania
- Stargazing in the Danube Delta
Equipment needed for stargazing
To begin your night sky observing adventure, the right tools will help you have a successful experience. An important tool is the telescope, which allows you to observe distant celestial objects such as planets, nebulae and galaxies in detail.
There are a variety of telescopes, from simple models for beginners to advanced instruments for amateur astronomers.
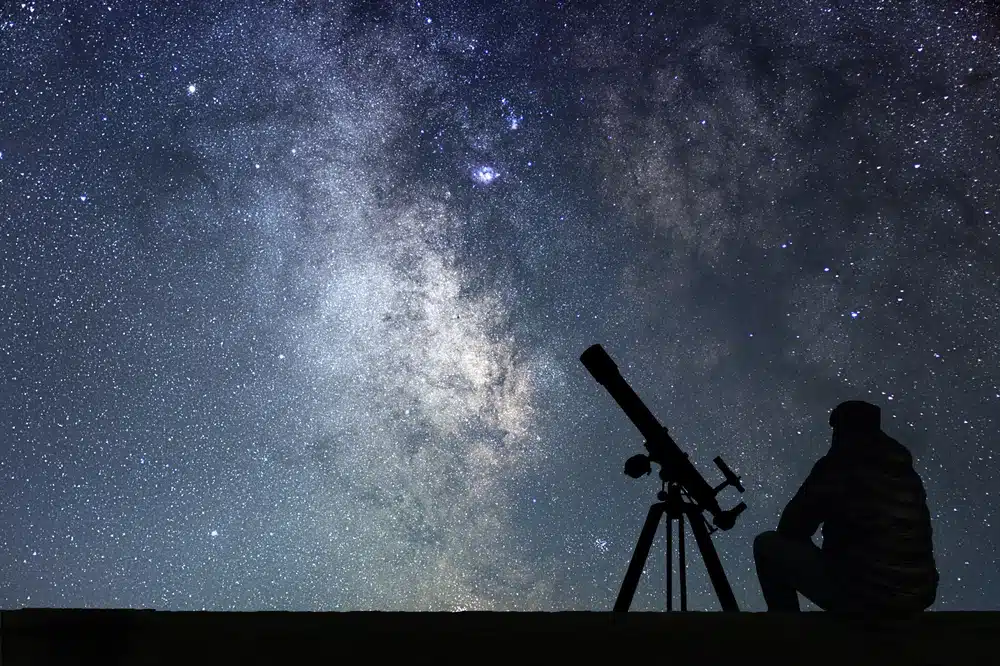

Amateur astronomer studying the sky with a telescope
An affordable and portable alternative to a telescope is astronomical binoculars.
It gives a wider view of the sky and is ideal for observing constellations or the Milky Way.
Astronomical binoculars usually have a magnification power of between 7x and 10x, enough to make out details invisible to the naked eye.
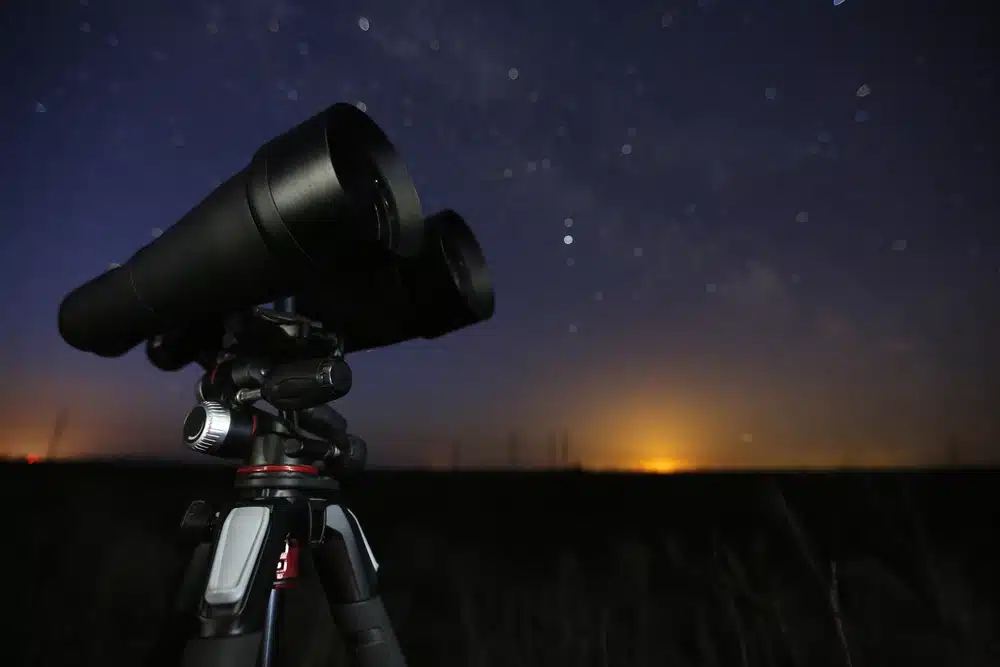

Astronomical binoculars for stargazing
A useful tool is a sky map, either in printed or digital format.
It helps you find your way around the sky and identify constellations and visible celestial objects.
Rotating sky maps, called planispheres, are handy because they can be adjusted for any date and time.
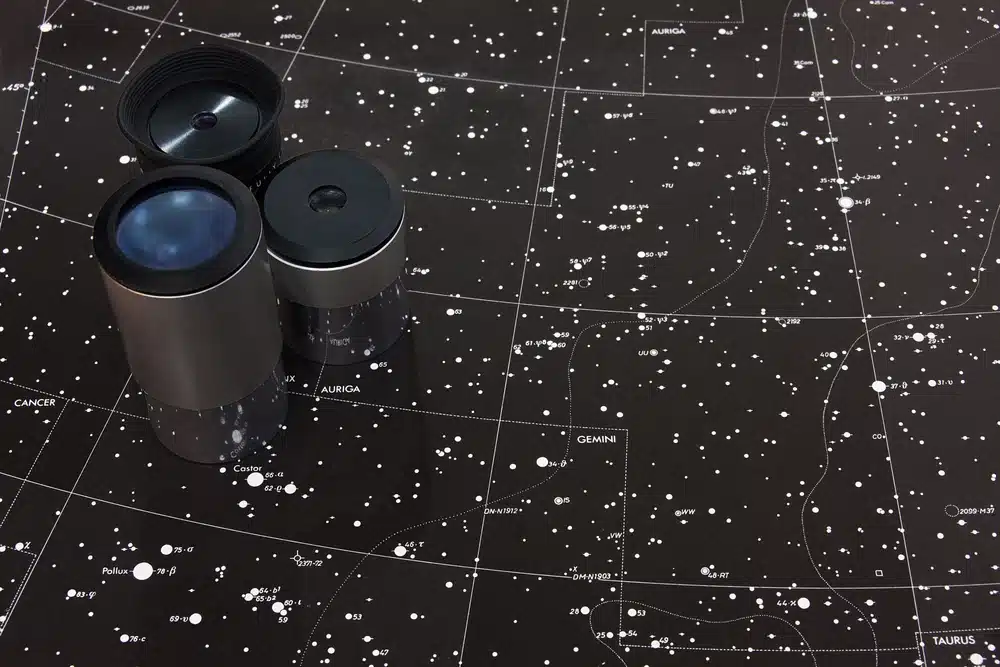
Sky map and telescope targets
In addition to this basic equipment, other useful accessories include:
- a red flashlight to keep your eyesight adapted to the dark;
- a comfortable chair for long observations;
- a smartphone app that provides real-time information about the night sky;
- a diary to record your observations.

Stargazing with digital star chart and telescope
With this basic equipment, you’ll be ready to explore the wonders of the night sky and enjoy the fascinating experience of stargazing. As your passion grows, you can gradually add specialized instruments to your collection. Now that we know what we need, let’s turn our attention to our fascinating cosmic neighbor, the Moon.
▶️ If you want to explore the magic of the Universe and enjoy an authentic experience in the heart of the Delta, Green Dolphin Camping is the perfect choice, offering the comfort and tranquility you need in a natural setting suitable for stargazing.
Observing the Moon – our fascinating cosmic neighbor
The Moon is one of the most exciting celestial objects. As the closest celestial body to Earth, the Moon puts on an impressive show even without optical instruments. However, a telescope can reveal amazing details of the lunar surface.
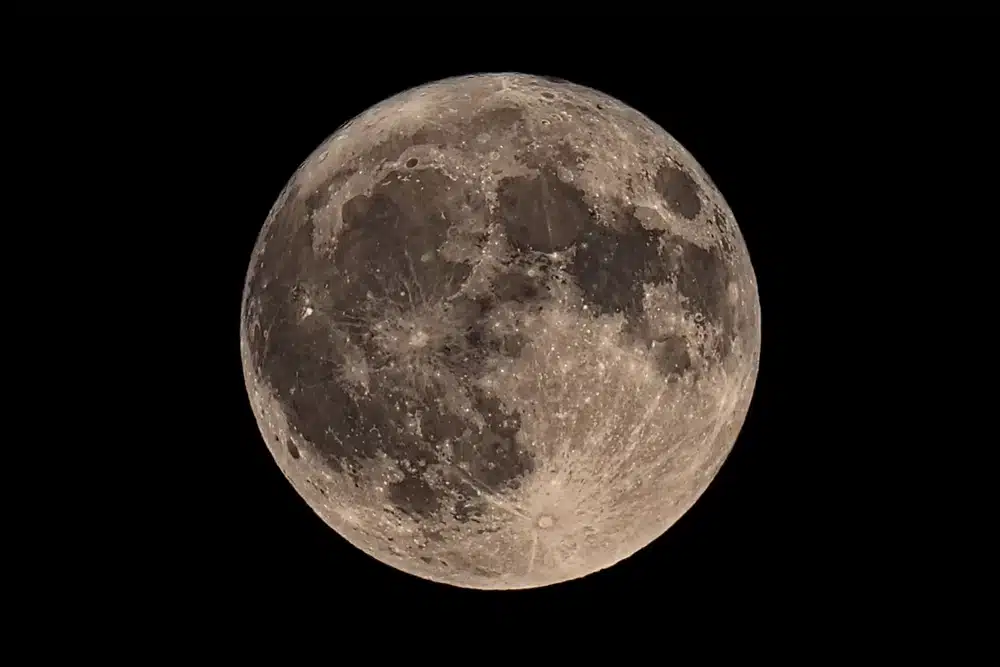

Stargazing - Moon through a telescope
One notable aspect of observing the Moon is the variation in its phases.
As the Moon orbits Earth, the illuminated portion visible from Earth changes, creating a complete lunar cycle of about 29.5 days.
This cycle begins with the New Moon, passes through First Quarter, reaches Full Moon and ends with Last Quarter, before returning to the New Moon.
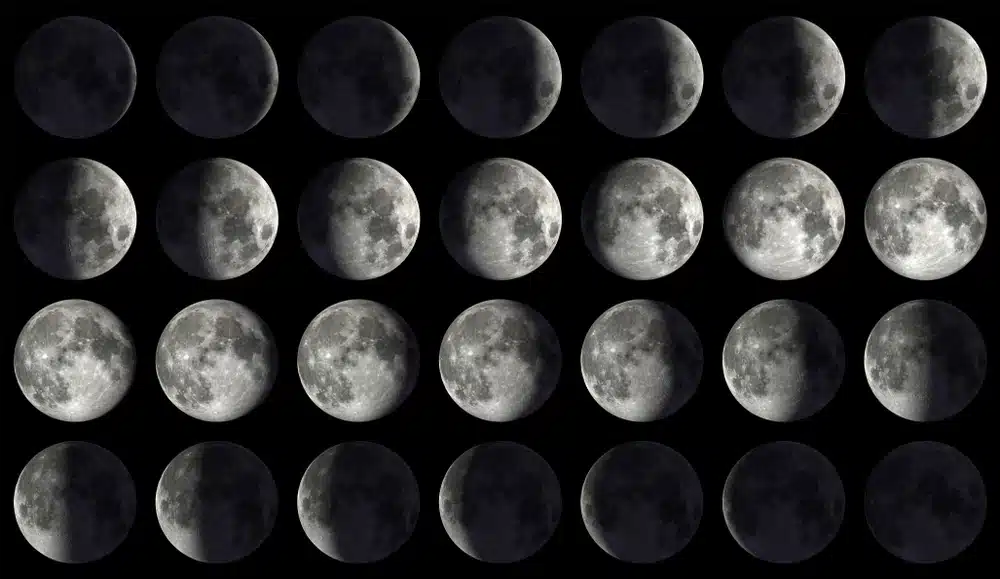

Stargazing - moon phases
Using a telescope to observe the Moon reveals a wealth of details:
- craters: circular formations resulting from meteorite impacts;
- lunar seas: dark areas formed by volcanic basalts;
- mountain ranges: such as the Apennines or the Carpathians;
- fissures and troughs: linear formations visible on the lunar surface.
An interesting feature of observing the Moon is the ‘terminator’ – the boundary between the bright and dark parts of the lunar surface. Along this line, the long shadows of the landforms create a strong contrast, providing opportunities to observe topographic details.
Many astronomical observatories organize public lunar observing sessions, providing opportunities for beginners to use high-performance telescopes and receive expert guidance. Observatories have specialized equipment such as CCD cameras or special filters that can enhance the experience.
For photography enthusiasts, the Moon is an ideal subject for astrophotography.
Even with a modest telescope and an ordinary digital camera, impressive images can be obtained.
Advanced techniques, such as image stacking, can produce spectacular results, revealing fine details of the lunar relief.
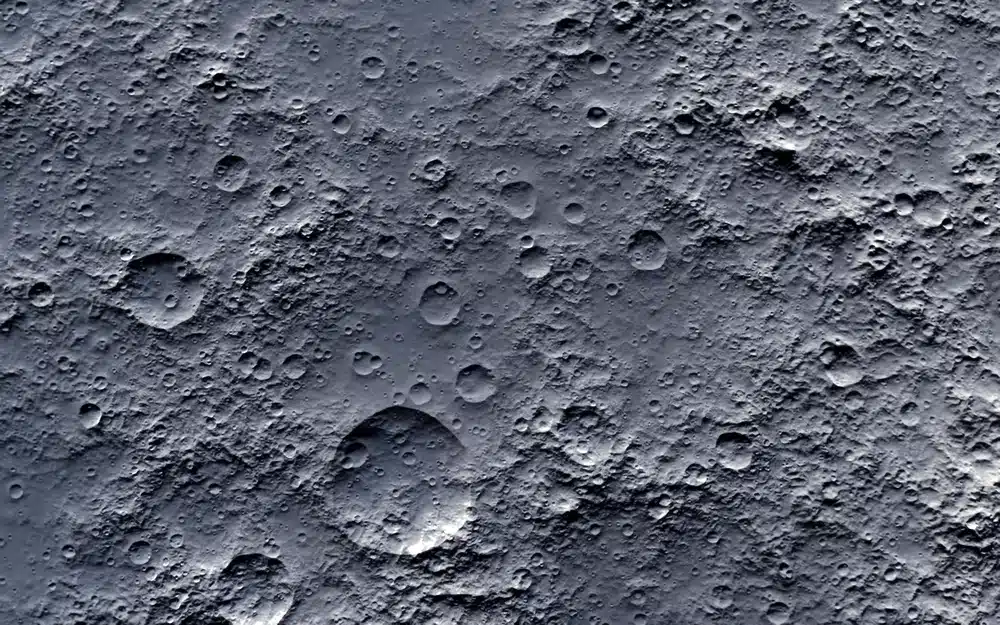

Stargazing - the Moon's detailed surface captured by astrophotography
Observing the Moon is an accessible activity for any astronomy enthusiast. From the naked eye to detailed telescope studies, the Moon continues to amaze and inspire curiosity about the Universe.
▶️ When you want to discover the beauty of our natural satellite, you need an experience at Green Dolphin Camping. Here you’ll have the opportunity to observe the skies from the surrounding canals and lakes, and relax on a stargazing session in a unique setting.
Exploring the Milky Way – our home galaxy
The Milky Way is a spectacle in the night sky and a great target for astronomers. This stripe across the celestial vault is the plane of the galactic disk seen from the inside.
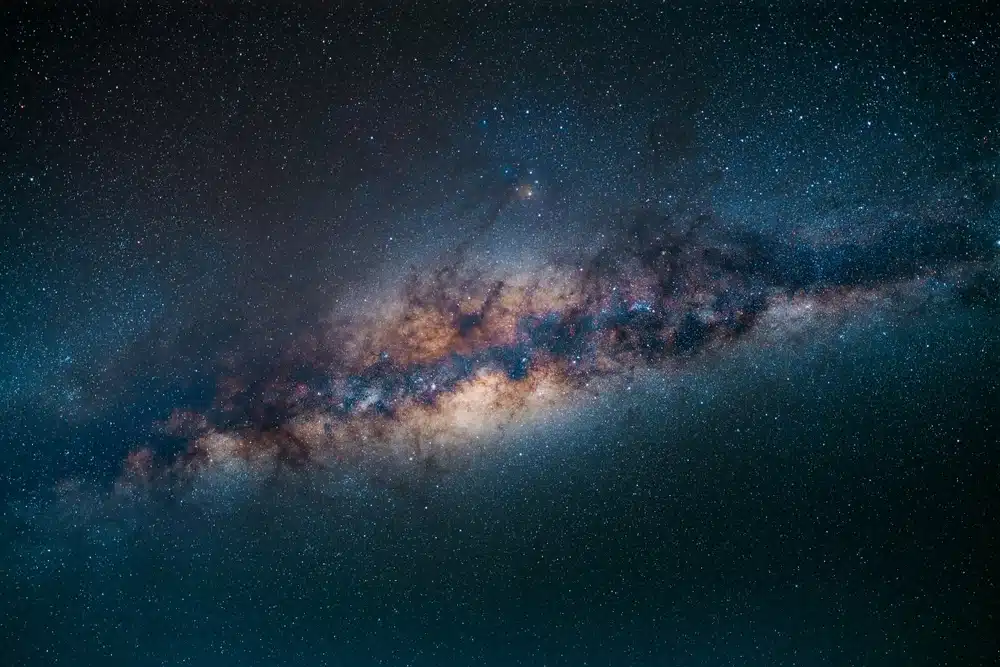

Stargazing - Milky Way
On clear nights, away from light pollution, the Milky Way appears as a diffuse streak dotted with millions of stars. The best times for observing are summers, when the galactic center is visible above the southern horizon.
To explore the Milky Way, it’s best to use a telescope or astronomical binoculars. These allow you to make out structures such as star clusters, nebulae and star-forming regions. Some notable objects include:
- globular cluster M13 in the constellation Hercules;
- the Lagoon nebula (M8) in Sagittarius;
- the Trifid nebula (M20) in Sagittarius;
- the Pleiades open swarm in Taurus.
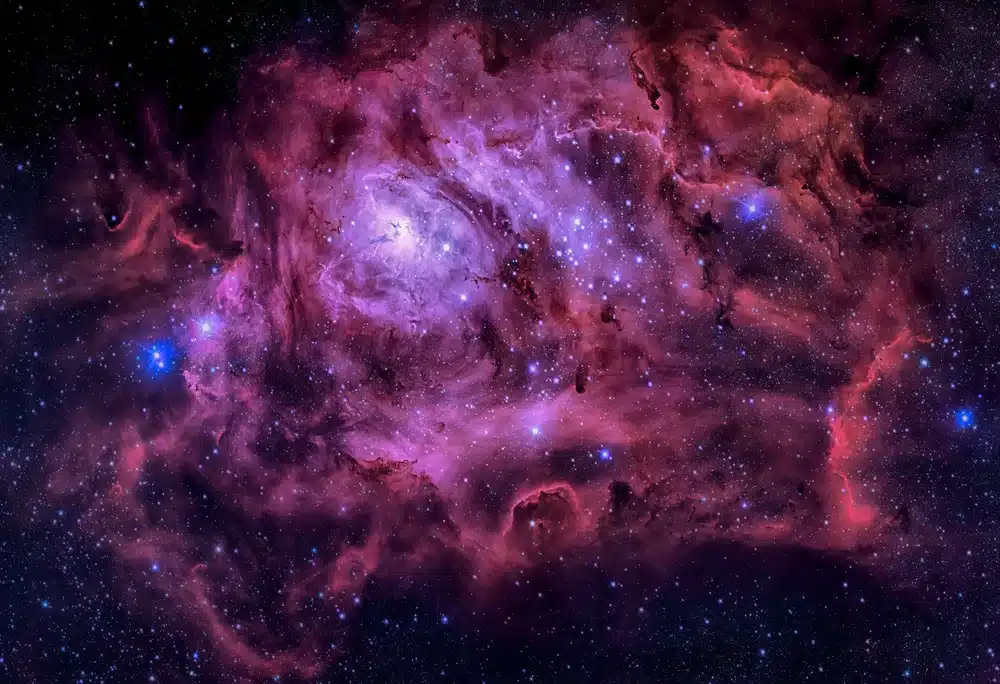

Stargazing - nebuloasa Laguna
As well as observing the Milky Way, the night sky offers phenomena such as shooting stars, meteors that burn up in the Earth’s atmosphere. Annual meteor showers, such as the Perseids in August, are excellent times to admire this phenomenon.
To find your way around the night sky, it’s useful to learn the main visible constellations. Some of the most easily recognizable include:
- Big Dipper;
- Orion (The Hunter);
- Cassiopeia;
- Scorpio.
Exploring the Milky Way is an exciting activity. With patience, you will discover more and more fascinating details of our galaxy.
Spectacular astronomical phenomena – eclipses and meteor showers
The night sky offers astronomical spectacles, including eclipses and meteor showers. These astronomical events attract the attention of amateur astronomers and the public.
Eclipses are rare events that occur when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun (solar eclipse) or when the Earth casts its shadow on the Moon (lunar eclipse). A total solar eclipse, when the Moon completely covers the solar disk, is an impressive astronomical phenomenon.
Meteor showers are another spectacular astronomical event. They occur when the Earth passes through a region of space with dust particles left by comets. The best-known meteor showers include:
- Perseids: visible in August, with a maximum of about 60 meteors per hour;
- Leonids: in November, sometimes producing “storms” of meteors;
- Geminids: in December, considered one of the most spectacular annual showers.
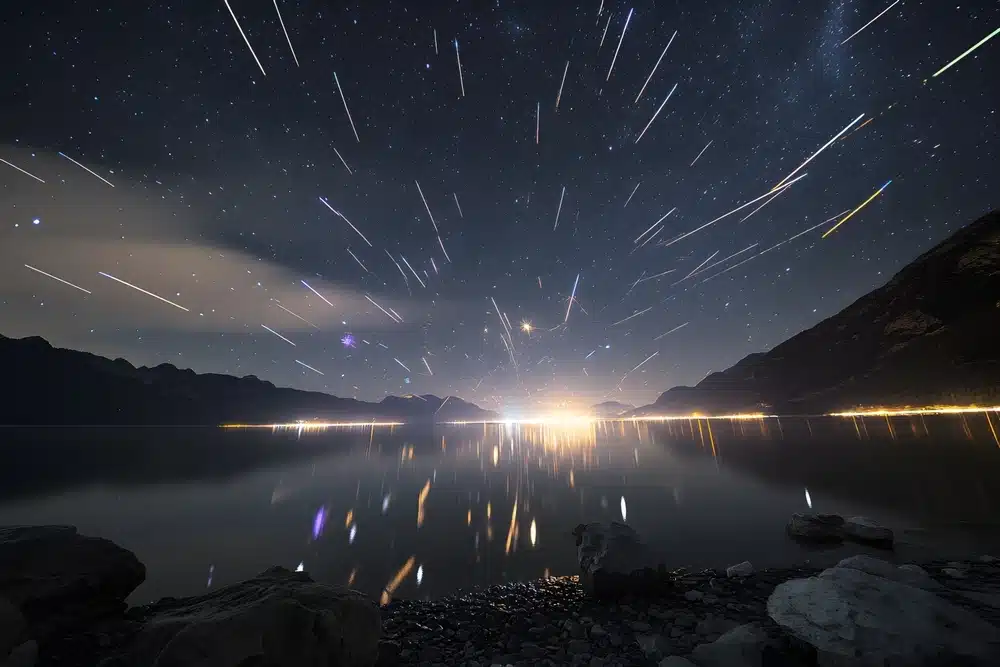

Stargazing-Perseids
To observe these astronomical phenomena, choose a place with dark skies, away from light pollution.
Also check the weather forecast to make sure the sky will be clear.
Observing an eclipse requires eye protection, especially for solar eclipses.
For meteor showers, observing with the naked eye is best, as meteors can appear anywhere in the sky.
These astronomical events provide opportunities for astrophotography. With the right equipment, you can capture images of the sun’s corona during an eclipse or bright trails of meteors.
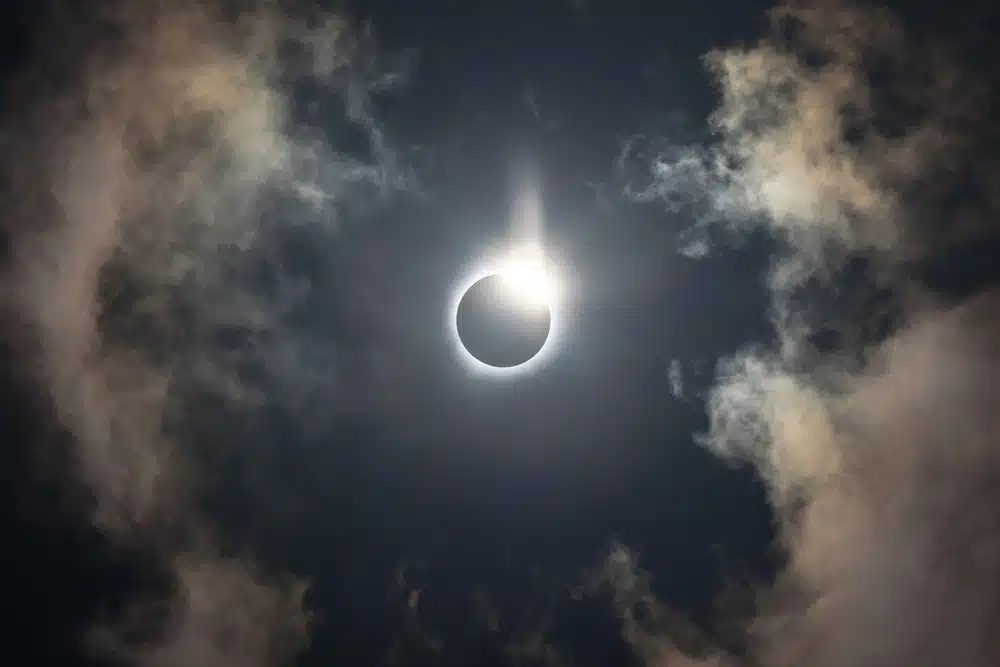

Stargazing - a total solar eclipse, an impressive astronomical phenomenon
The annual astronomical calendar includes many such phenomena, providing opportunities to admire the night sky. Whether you’re an experienced observer or a beginner, eclipses and meteor showers remain exciting experiences.
▶️ If you are planning to go stargazing in the Danube Delta, at Green Dolphin Camping you will find accommodation in cottages, fresh air and tranquility. Equipped with the bare essentials, with a separate entrance and a small patio, they’re just what you need for a getaway at the Danube’s spill into the sea.
Best locations for stargazing in Romania
To observe the beauty of the night sky, it’s essential to find locations with dark skies, away from light pollution. In Romania, there are stargazing areas that offer optimal conditions to admire the stars, planets and the Milky Way.
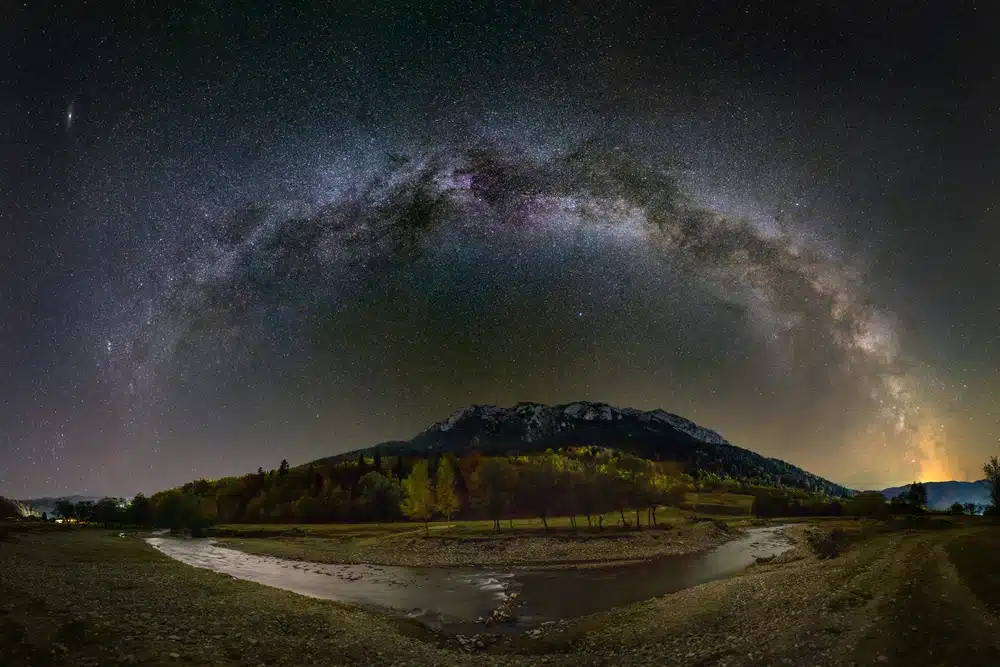

Stargazing - starry sky over the Piatra Craiului mountains
A popular destination is the Retezat National Park. Situated in the Southern Carpathians, this park offers some of the darkest skies in the country, ideal for observing celestial objects. Lake Bucura is a favorite spot for stargazing in the park.
Another option is the Măcin Mountains in Dobrogea. Far from the big cities, this region benefits from dark skies, perfect for astronomy. Mount Țuțuiatu offers a spectacular view of the night sky.
For those looking for facilities, the astronomical observatory in Barlad is a top destination. Equipped with telescopes and organizing public sessions, this astronomical observatory offers opportunities to explore the sky alongside experts.
In Transylvania, the Apuseni Mountains are a popular choice. The karst plateau of Padiș, with its altitude and distance from sources of light pollution, offers ideal conditions.
For those who prefer affordable locations, Dolphin Camping in the Danube Delta is an option. Situated in an area with dark skies, this campsite organizes stargazing sessions and offers equipment for observing the sky.
Wherever you are, check the weather forecast and choose moonless nights. With planning, you’ll be able to admire the starry skies away from the city lights.
Stargazing in the Danube Delta
The Danube Delta, one of the most isolated and poorly lit regions in Romania, offers exceptional conditions for observing the night sky.
Thanks to the almost total lack of light pollution in the central areas of the Delta, the sky is remarkably clear, allowing for a wide visibility of astronomical objects with the naked eye.
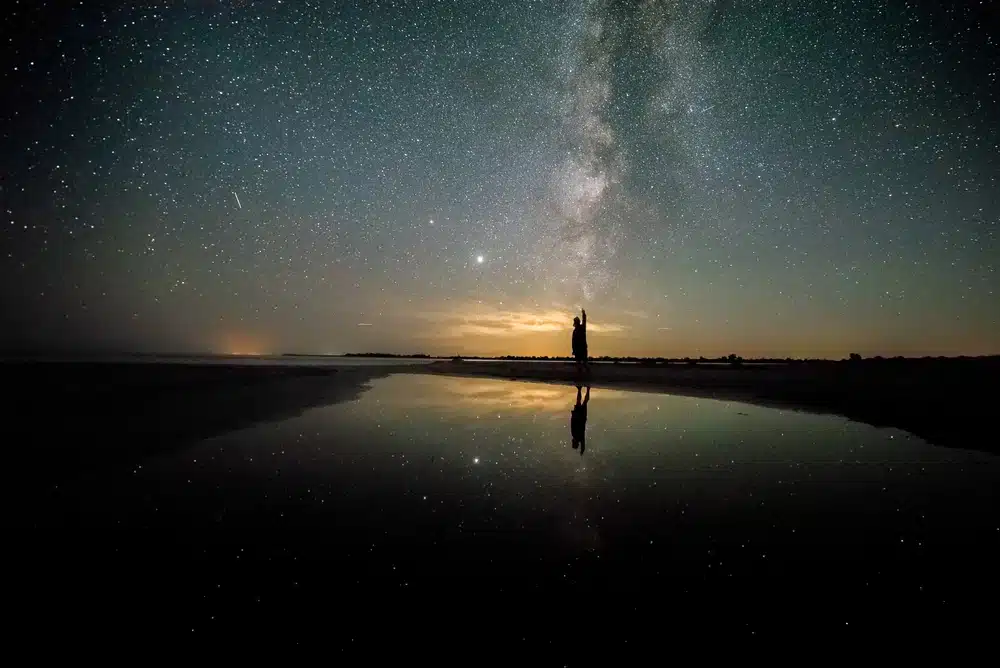

Stargazing - Starry skies in the Danube Delta
During the summer, when the nights are clear and the temperatures are favorable for outdoor activities, the skies over the Delta become a natural planetarium. The Milky Way is easily visible, stretching like a band of light across the sky from northeast to southwest. This is actually the disk of our galaxy, seen from within, made up of billions of stars, nebulae and interstellar dust.
The most visible constellations of summer include:
- Cygnus (Swan), which lies at the very center of the Milky Way and is easily recognizable by its cross shape;
- Lyra (Lyra), which contains the star Vega, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and part of the stars that make up the Summer Triangle;
Aquila (Eagle), with the star Altair, and Delphinus (Dolphin), a smaller but distinct constellation nearby.
A notable celestial phenomenon in summer is the Perseid meteor shower, which peaks around August 12-13. These meteors originate from the remnants of the Swift-Tuttle comet and can be observed at a frequency of up to 60-100 meteors per hour in ideal conditions, such as those offered by the Danube Delta.
Also, the visible planets vary from year to year, but generally on summer evenings they can be seen:
- Jupiter and Saturn, the two gas giants, visible as very bright dots, sometimes even in detail through a small telescope;
- Mars and Venus, depending on their position in relation to the Earth, may appear at dawn or in the evening, with Venus often referred to as the “Evening Star” or “Morning Star”.
Another remarkable aspect during a stargazing session in the Delta is the low background noise and the natural static environment, which helps the eyes adapt to the darkness and observe the deep sky in detail.
The Danube Delta offers an ideal setting for observing astronomical phenomena and is one of the best locations in south-eastern Europe for stargazing. This region combines a protected natural environment with high-quality skies, making any observing session both informative and memorable.
Exploring the night sky in Romania offers a wealth of opportunities for stargazing, from observing the Moon and the Milky Way to watching eclipses and meteor showers. Whether you’re an amateur astronomer or a simple nature lover, there are places and events that will captivate you. Plan your next astronomical adventure and enjoy the beauty of the universe.
Photo source: Shutterstock.com